miRTargetLink Human offers detailed information on human microRNA-mRNA interactions in the form of interactive interaction networks. Perform a microRNA or target gene search in the search areas on the right to get started, or view the manual.
Data and features
The interaction networks generated by miRTargetLink contain experimentally validated interactions as present in the latest version of miRTarBase1 (Release 6.0: Sept. 15, 2015) as well as from in-house generated data. Next to these experimentally validated interactions, false positive interactions will be integrated into miRTargetLink. These are interactions that were experimentally verified not to participate in the predicted interaction. The data on these false leads will be of great value for researchers in genetics and related fields and is collected and continuously updated by the people of the Chair for Clinical Bioinformatics at the University of Saarland.
Networks
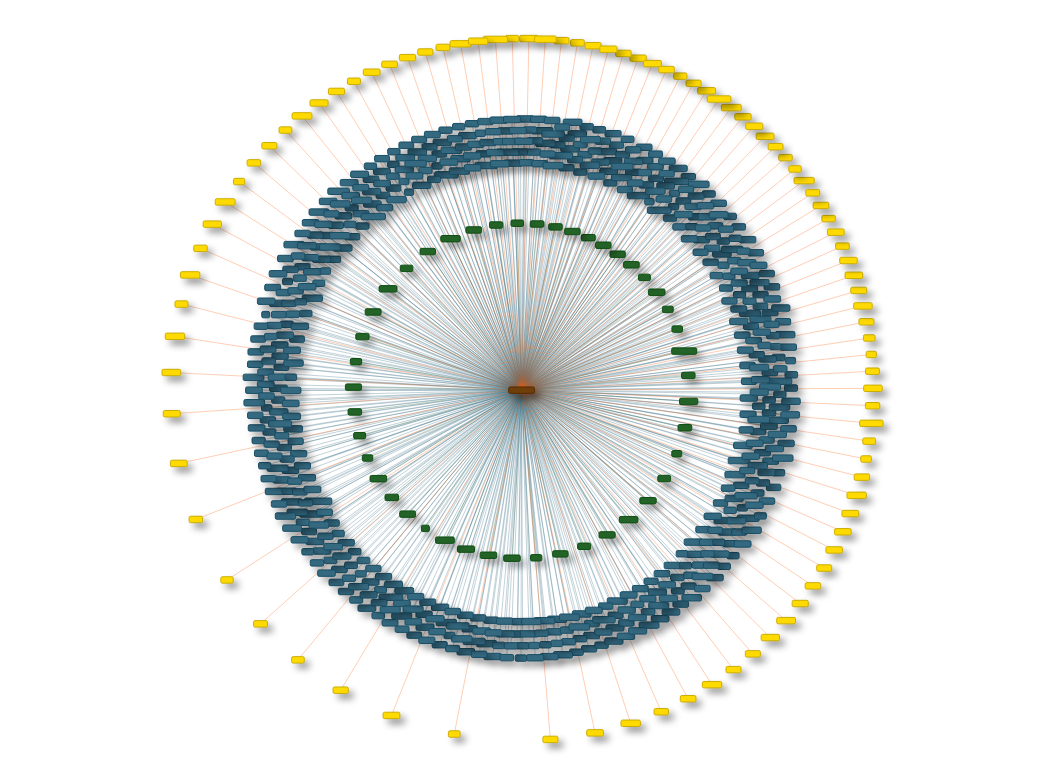
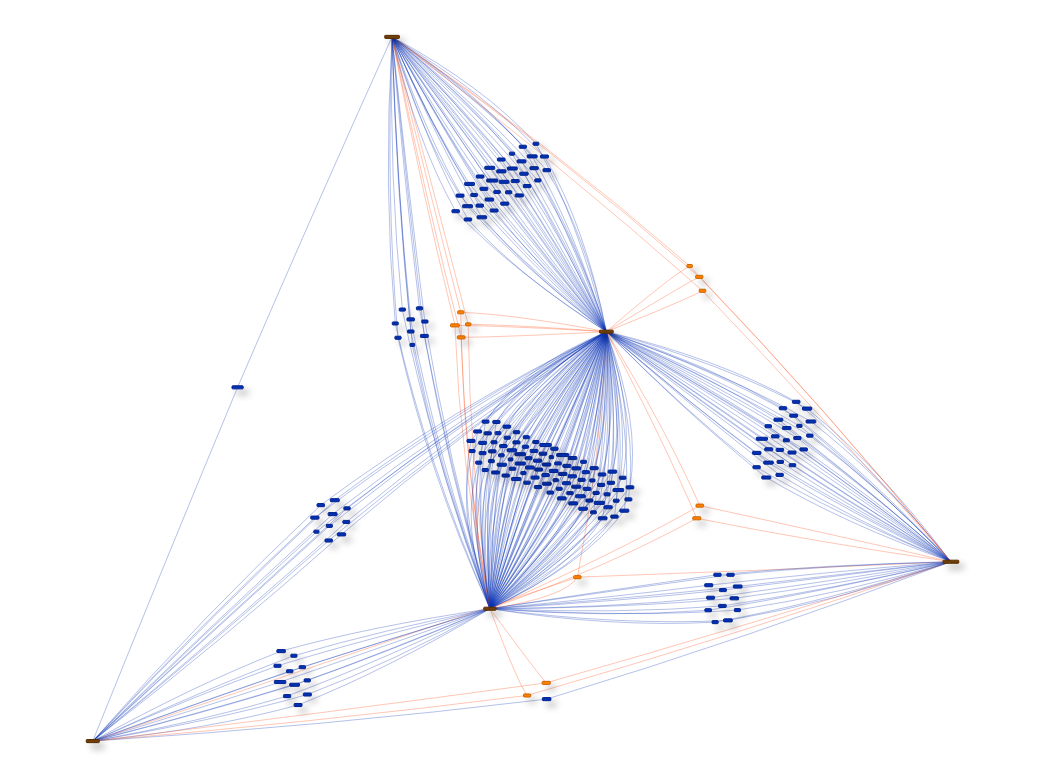
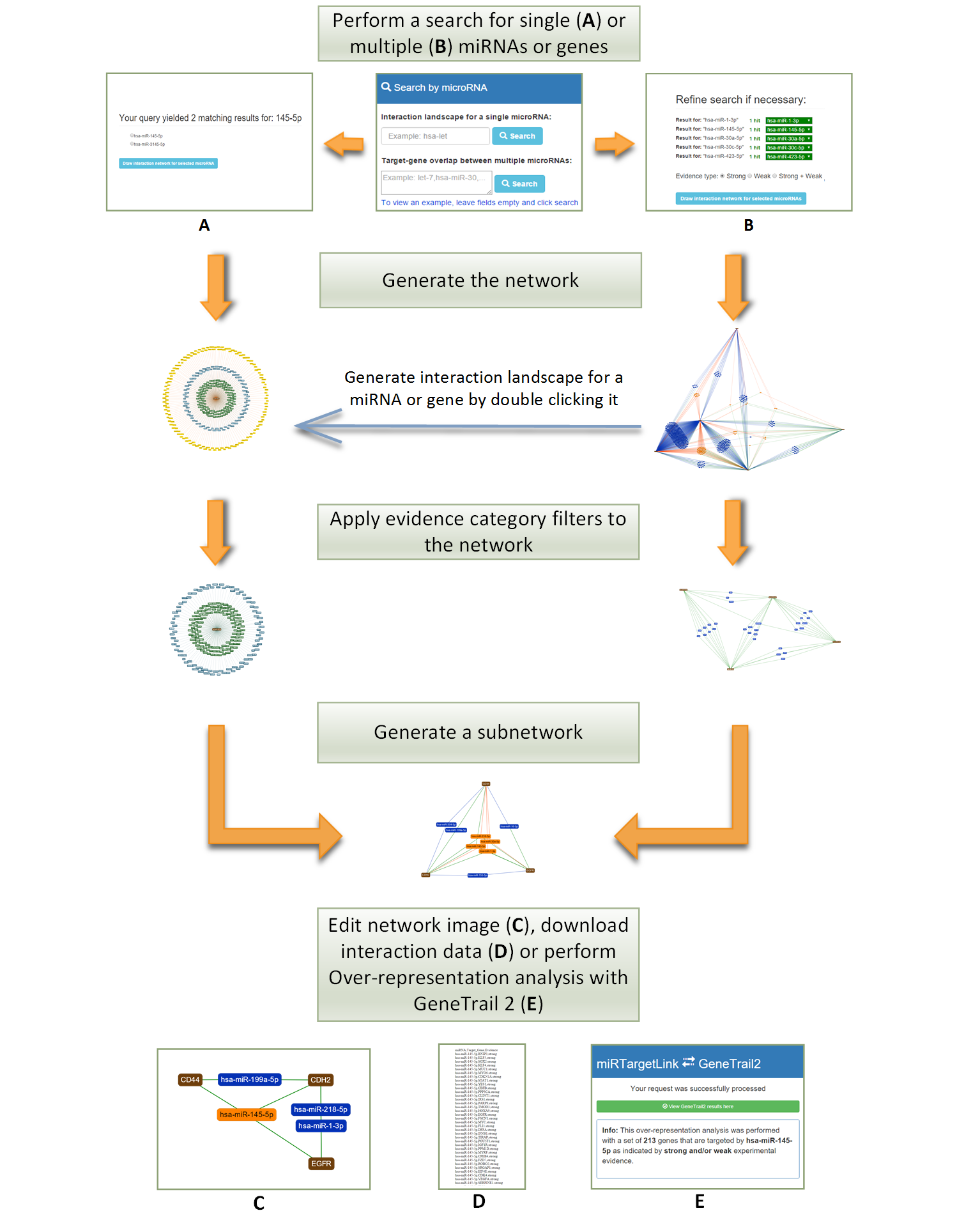
There are two types of networks that can be generated by miRTargetLink. Firstly, for single microRNA or gene queries it can generate an interaction landscape which is a 'one to many' visualization of the complete interaction library for that specific microRNA or Gene. This view shows information about the experimental support for each interaction in the landscape. Secondly, for queries with multiple microRNAs or genes it can generate a 'many to many' interaction network showing the complete set of (experimentally validated) interactions that are overlapping between the query microRNAs or genes. It is possible to switch between these two views at any time by selecting nodes and generating their individual interaction landscape or (sub)network.
Predictions
The included predicted targets were generated with miRanda, more microRNA target prediction algorithms will be integrated in the next version of miRTargetLink.
| Link | Citation |
|---|---|
| miRanda | Full text PDF |
| ... | ... |
If you make use of miRTargetLink please cite:
Hamberg, M., Backes, C., Fehlmann, T., Hart, M., Meder, B., Meese, E., & Keller, A. (2016). miRTargetLink-miRNAs, Genes and Interaction Networks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(4). http://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040564
Free Full-Text
To view an example, leave fields empty and click search
To view an example, leave fields empty and click search
How to cite